In the past few posts I have written how to do some basic setup tasks once you have a OpenShift deployment up and running. I figured I should backpedal a little here and discuss how to do a custom OpenShift deployment on VMWare using the IPI deployment method.
To start when you do a basic deployment of OpenShift with the openshift-install binary you get a basic cluster with 3x supervisor nodes and 3x worker nodes. While this is great for folks interested in just getting to know OpenShift, if you are deploying production workloads you may want to increase the supervisor/worker node counts.
By default the 3x worker nodes are deployed 2x CPU counts with a single core on each socket, 8GB of RAM, and 120GB hard drive. Well if you wanted to increase these default values, you are in luck; I will detail that process below!
First we need to create a directory to hold our custom install-config.yml and installation files for our cluster.
mkdir install-dirNext we want to create our custom install-config.yml used to spin up our custom OpenShift cluster deployment. We can do this using the openshift-install cli tool by running the following command and filling in all the necessary information about our VMWare cluster and our OpenShift cluster we are deploying.
openshift-install create install-config --dir=./install-dir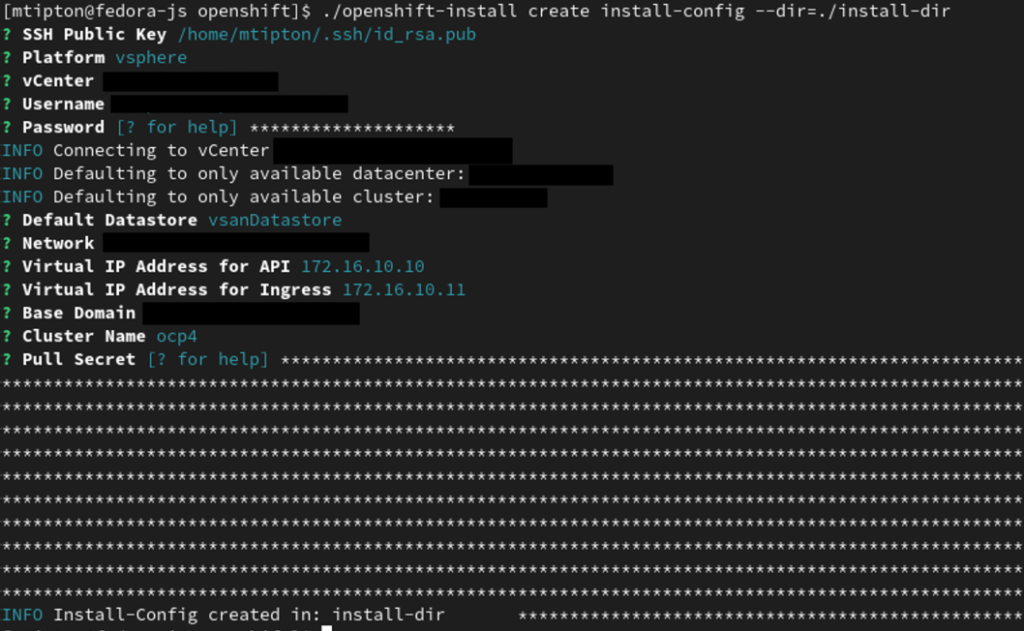
Next we need to edit the newly created install-config.yml in the installation directory we created. It will look like the snippet below in the screenshot. Notice the platform variable is set to {}, we will need to edit this to have the proper amount of resources we want to give our OpenShift cluster VMs.
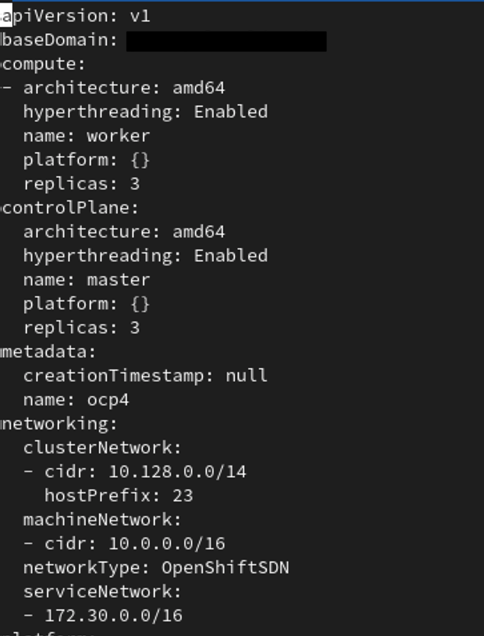
To do this all we need to do is remove the {} and add some new variables to our yaml file to specify the platform (vsphere in this example), cpus, coresPerSocket, memoryMB, and diskSizeGB. Below you will see an example of deploying supervisor and worker nodes with 3 replicas each with 4 CPUs, 2 cores per socket, 16GB of RAM, and 120GB hard drives.
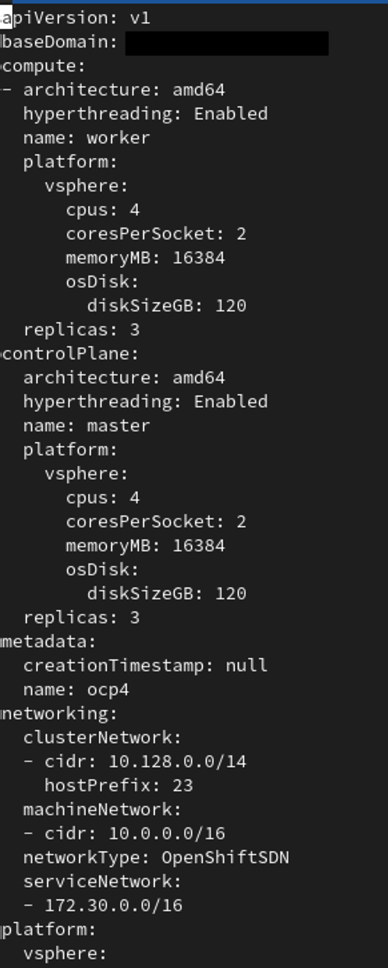
After you have edited the install-config.yml just go ahead and write the file and now we can run the create cluster command to deploy our custom configured OpenShift install.
openshift-install create cluster --dir=./install-dirEnjoy your newly customized OpenShift cluster!
-Mike